Understanding Space Weather and Its Impact
Explore the intriguing world of space weather and how it affects our planet. These insights into space and weather will broaden your understanding of the dynamic relationship between the two. Here are some key facts:
What is Space Weather?
- Space weather refers to conditions on the Sun and in the solar wind.
- It impacts the space environment around Earth.
Solar Flares and Their Effects
- Solar flares are explosive releases of energy from the Sun’s surface.
- They occur when magnetic energy in the solar atmosphere is suddenly released.
- These flares emit intense radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum.
Aurora Borealis and Aurora Australis
- The Northern Lights and Southern Lights are influenced by space conditions.
- Charged particles from the solar wind collide with Earth’s magnetosphere.
- These collisions create luminous colors in the polar regions.
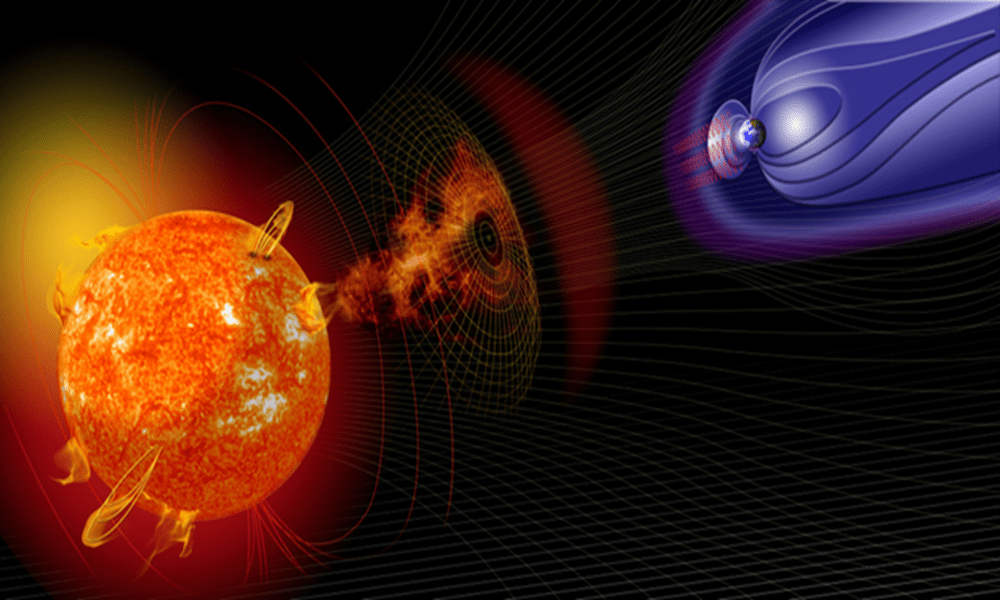
The Role of the Solar Wind
- The solar wind is a continuous stream of charged particles from the Sun.
- It interacts with Earth’s magnetosphere.
- This interaction influences geomagnetic conditions and space phenomena.
Geomagnetic Storms
- Geomagnetic storms result from disturbances in the solar wind.
- They interact with Earth’s magnetic field.
- These storms can impact communication systems, navigation devices, and power grids.
The 11-Year Solar Cycle
- The Sun undergoes an 11-year solar cycle.
- This cycle is characterized by variations in sunspot activity.
- Sunspots contribute to solar flares and coronal mass ejections, influencing space conditions.
Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs)
- CMEs are massive bursts of solar wind and magnetic fields.
- They rise above the solar corona or are released into space.
- When directed toward Earth, CMEs can trigger geomagnetic storms.
Solar Maximum and Solar Minimum
- The Sun experiences periods of increased and decreased activity during the solar cycle.
- Solar maximum refers to the phase with high sunspot numbers and intense solar flares.
- Solar minimum is a period of reduced activity.
Solar Proton Events
- Solar proton events involve high-energy protons emitted by the Sun during solar flares.
- These events pose radiation hazards to astronauts and can impact satellite electronics.
- Monitoring space weather is crucial for space missions.
Forecasting Space Conditions
- Space weather forecasting predicts solar activity and its effects on Earth and space-based systems.
- Scientists use observations and models to provide warnings about solar flares and geomagnetic storms.
The Heliosphere
- The heliosphere is a vast region influenced by the solar wind.
- It extends far beyond Pluto.
- It acts as a protective bubble, shielding our solar system from galactic cosmic rays.
Conclusion:
Understanding space weather is essential for safeguarding our technology and infrastructure. The interplay between space and weather affects everything from communication systems to power grids. By learning more about it, we can better prepare for its impacts and protect our planet.















